How Do Solar Panels Work The Science Of Solar Explained
We all know that solar photovoltaic panels transform sunlight into useable electricity, but few people know the actual science behind the process. This week on the blog we are going to get into the nitty-gritty science behind solar. It can seem complicated, but it all boils down to the photovoltaic effect the ability of matter to emit electrons when bathed in light.
Before we get to the molecular level, lets take a high-level look at the basic flow of electric generation:
Are Solar Panels Environmentally Friendly To Make
While solar power is often held up as a beacon of clean energy in a world rapidly succumbing to climate change, detractors will point out that solar panel manufacturing has its own environmental considerations.
As solar panel technology has improved over the last several decades, the manufacturing process has continued to become less polluting, as shown in an academic study that found strong downward trends of environmental impact from solar panel production between 1975 and 2015. That rate of improvement hasnt stalled in recent years, and identifying the most environmentally friendly materials and production processes remains a top priority of all major solar producers.
Even further, end-of-life considerations for solar panels are being actively incorporated into the solar panel lifecycle, with manufacturers developing ways to recycle panels and their material components to further minimize their impact. With that said, there is no such thing as a free lunch.
The manufacturing of any product requires energy and resources, meaning the process inherently adds carbon dioxide to the atmosphere exactly what that renewable energy is seeking to minimize. While its true that solar panels have an environmental cost to their production, so too do the construction of power plants and wind turbines the extraction and burning of fossil fuels and any other method to create useful energy.
The Materials Found In Solar Cells
Here are the main materials that make up the solar cells in each panel.
Monocrystalline cells
Monocrystalline solar cells are made from single crystalline silicon. They have an incredibly distinctive appearance, as they are often coloured. The cells themselves also tend to have quite a cylindrical shape.
So that they can keep the costs low and the performance at optimal levels, manufacturers tend to cut out the four sides of the monocrystalline cells. While this gives them their recognisable appearance, it is also quite a wasteful process. They tend to have the highest levels of efficiency and are considered the highest quality of the three main types of material.
Polycrystalline Solar Cells
Polycrystalline solar panels were first introduced to the public in 1981. Unlike their monocrystalline counterparts, polycrystalline cells do not require each of the four sides to be cut which results in less waste.
Instead of cutting, the silicon is melted and poured into square moulds. These then result in perfectly shaped square cells. The polycrystalline solar panel is considered to be the mid-range panels in terms of price and efficiency out of the three main materials used.
Thin Film Solar Cells
- Amorphous silicon
Recommended Reading: What Are The Government Incentives For Solar
How Do Solar Panels Work
To understand how silicon solar panels make electricity, you must think down at the atomic level. Silicon has an atomic number of 14, which means it has 14 protons in its center and 14 electrons circling that center. Using the classic imagery of atomic circles, there are three circles moving around the center. The innermost circle is full with two electrons, and the middle circle is full with eight.
However, the outermost circle, which holds four electrons, is half-full. That means it will always look to fill itself up with help from nearby atoms. When they connect, they form what is called a crystalline structure.
With all those electrons reaching out and connecting to each other, there isn’t much room for an electric current to move. That’s why the silicon found in solar panels is impure, mixed in with another element, like phosphorous. The outermost circle of phosphorous has five electrons.
That fifth electron becomes what is known as a “free carrier,” able to carry an electrical current without much prodding. Scientists boost the number of free carriers by adding impurities in a process called doping. The result is what’s known as N-type silicon.
Additional Important Parts To Solar Panels
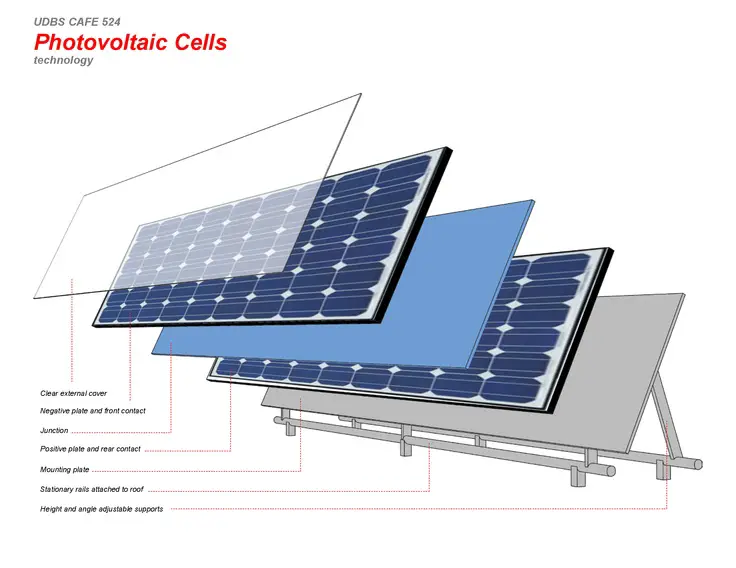
Aside from their silicon solar cells, a typical solar module includes a glass casing that offers durability and protection for the silicon PV cells. Under the glass exterior, the panel has a layer for insulation and a protective back sheet, which protects against heat dissipation and humidity inside the panel. This insulation is important because increases in temperature will lead to a decrease in efficiency, resulting in lower solar panel performance.
Solar panels have an anti-reflective coating that increases sunlight absorption and allows the silicon cells to receive maximum sunlight exposure. Silicon solar cells are generally manufactured in two cell formations: monocrystalline or polycrystalline. Monocrystalline cells are made up of a single silicon crystal, whereas polycrystalline cells are made up of fragments or shards of silicon. Mono formats provide more room for electrons to move around and thus offer a higher efficiency solar technology than polycrystalline, though they are typically more expensive.
Also Check: What Is The Average Cost Of A Solar Panel System
The Efficiency Of Photovoltaic Systems Varies By The Type Of Photovoltaic Technology
The efficiency at which PV cells convert sunlight to electricity varies by the type of semiconductor material and PV cell technology. The efficiency of commercially available PV modules averaged less than 10% in the mid-1980s, increased to around 15% by 2015, and is now approaching 20% for state-of-the art modules. Experimental PV cells and PV cells for niche markets, such as space satellites, have achieved nearly 50% efficiency.
What Are Solar Panels Made Of And How Are They Made
As solar energy becomes increasingly popular for residential use, youve probably had a few neighbors install solar panels and may even be thinking of getting a system for your own home. But before adopting this technology, you may be wondering: What are solar panels made of, and how are they made?
Many people simply accept that solar panels work and thats all we need to know about them, but for the scientifically and technologically curious, each individual solar panel contains a world of interesting components and materials.
Keep reading to learn more about what actually makes up a solar panel, or click below to get more information from a top solar installer.
Also Check: How Much Does It Cost To Go Completely Solar
Use Of Tracking Angle In Solar Panels Production
The tracking angle tells us what angle the solar panel needs to absorb the optimal amount of light. This angle is dependent on the angle of incidence, which is the angle between the line that points to the sun and the angle of the solar panel. If your Reno solar installer is worth its weight in gold, theyll know the difference between these two mechanisms.
You want to minimize this angle as much as possible to get maximum light exposure and absorption from your solar panels. The angle of the sun compared to the earth depends on time, not just the time of day, but the season within the year as well.
Most residential systems are stationary. Stationary panels depend on an angle of incidence that maximizes light absorption the majority of the year. The EIA has found that south is the best direction for a stationary photovoltaic panel to tilt.
How Much Energy Can We Get From The Sun
Solar power is amazing. On average, every square meter of Earth’ssurface receives 163 watts of solar energy . In other words, you could stand a really powerful table lamp on every square meter ofEarth’s surface and light up the whole planet with the Sun’s energy! Or, to putit another way, if we covered just one percent of the Sahara desert with solarpanels, we could generate enough electricityto power the whole world. That’s the good thing about solar power:there’s an awful lot of itmuch more than we could ever use.
But there’s a downside too. The energy the Sun sends out arrives onEarth as a mixture of light and heat. Both of these are incrediblyimportantthe light makes plants grow, providing us with food, whilethe heat keeps us warm enough to survivebut we can’t use either theSun’s light or heat directly to run a television or a car. We have tofind some way of converting solar energy into other forms of energy wecan use more easily, such as electricity. And that’s exactly what solarcells do.
Read Also: Can I Run An Air Conditioner On Solar Power
What Are Solar Panels Made Of
The materials used to manufacture the cells for solar panels are only one part of the solar panel itself. The solar panel manufacturing process brings together six different components to create a functioning solar panel. These parts include silicon solar cells, a metal frame, glass sheet, standard 12V wire, and bus wire. If you are DIY-minded and curious about solar panel materials, it may even be a question of wanting a hypothetical ingredients list to produce one on your own. Here are the common parts of a solar panel explained:
Research And Industrial Production
Research into solar power for terrestrial applications became prominent with the U.S. National Science Foundation’s Advanced Solar Energy Research and Development Division within the “Research Applied to National Needs” program, which ran from 1969 to 1977, and funded research on developing solar power for ground electrical power systems. A 1973 conference, the “Cherry Hill Conference”, set forth the technology goals required to achieve this goal and outlined an ambitious project for achieving them, kicking off an applied research program that would be ongoing for several decades. The program was eventually taken over by the Energy Research and Development Administration , which was later merged into the U.S. Department of Energy.
Following the 1973 oil crisis, oil companies used their higher profits to start solar firms, and were for decades the largest producers. Exxon, ARCO, Shell, Amoco and Mobil all had major solar divisions during the 1970s and 1980s. Technology companies also participated, including General Electric, Motorola, IBM, Tyco and RCA.
Recommended Reading: Do You Get Paid For Having Solar Panels
Silicon Wafers And Solar Cells
Once the crystal seed has become silicon ingots, the next step of the manufacturing process is to slice them into thin disks. These are the silicon wafers. Silicon wafers are treated to create solar cells.
Moreover, metal conductors are added to them as well. These conductors are the grid-like matrix, which you can see on the surface of the solar cells. This conductor matrix would ensure that electrons will efficiently travel into the output cables, thus, producing electricity flow.
Solar Photovoltaic Cell Basics
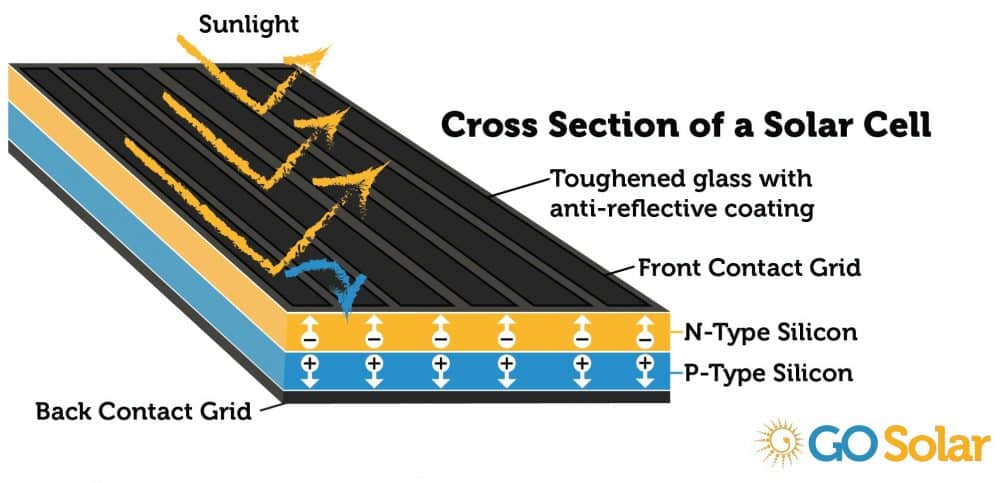
When light shines on a photovoltaic cell also called a solar cell that light may be reflected, absorbed, or pass right through the cell. The PV cell is composed of semiconductor material the semi means that it can conduct electricity better than an insulator but not as well as a good conductor like a metal. There are several different semiconductor materials used in PV cells.
When the semiconductor is exposed to light, it absorbs the lights energy and transfers it to negatively charged particles in the material called electrons. This extra energy allows the electrons to flow through the material as an electrical current. This current is extracted through conductive metal contacts the grid-like lines on a solar cells and can then be used to power your home and the rest of the electric grid.
The efficiency of a PV cell is simply the amount of electrical power coming out of the cell compared to the energy from the light shining on it, which indicates how effective the cell is at converting energy from one form to the other. The amount of electricity produced from PV cells depends on the characteristics of the light available and multiple performance attributes of the cell.
Learn more below about the most commonly-used semiconductor materials for PV cells.
Silicon
Thin-Film Photovoltaics
Perovskite Photovoltaics
Organic Photovoltaics
Quantum Dots
Multijunction Photovoltaics
Concentration Photovoltaics
Don’t Miss: How To Start A Sole Proprietorship In Ny
Where Can I Buy Solar Panels
Well, right here on this website, of course!
Our solar panel brands include the most respected manufacturers in the solar panel business. These brands include such names as BP Solar, General Electric, and Sharp, among others. We feature only the highest quality solar panels from manufacturers with a proven track record in solar panel technology. With over 30 years in the solar panel business, you can be sure that at MrSolar.com, we know solar panels!
Save
A Short History Of Solar Panels
The development of solar energy goes back more than 100 years. In the early days, solar energy was used primarily for the production of steam which could then be used to drive machinery. But it wasn’t until the discovery of the “” by Edmond Becquerel that would allow the conversion of sunlight solar electric energy. Becquerel’s discovery then led to the invention in 1893 by Charles Fritts of the first genuine solar cell which was formed by coating sheets of selenium with a thin layer of gold. And from this humble beginning would arise the device we know today as the solar panel.
Russel Ohl, an American inventor on the payroll of Bell Laboratories, patented the world’s first silicon solar cell in 1941. Ohl’s invention led to the production of the first solar panel in 1954 by the same company. Solar panels found their first mainstream use in space satellites. For most people, the first solar panel in their life was probably embedded in their new calculator – circa the 1970s!
Today, solar panels and complete solar panel systems are used to power a wide variety of applications. Yes, solar panels in the form of solar cells are still being used in calculators. However, they are also being used to provide solar power to entire homes and commercial buildings, such as Google’s headquarters in California.
Read Also: Is Solar Good For My House
The Problem With Solar Panel Disposal
Most solar recycling plants simply remove the valuable silver and copper from the cells and then recycle the contaminated glass and plastic casing by burning them in cement ovens. Since the process is costly and time-consuming, its more convenient for solar companies to drop the dead panels into landfills or export them to third-world countries.
While a properly-built landfill should contain most hazardous material in the waste, a developing country may not have the infrastructure or regulations to properly dispose of imported solar panel waste. Potential leaching of these metals into the surrounding environment can pose a public health problem, especially in a nation without the necessary disposal infrastructure. As society continues to adopt solar power, this problem may worsen in the coming decades, with almost 80 million tons of solar waste projected by 2050.
Studies have shown the heavy metals in solar panels namely lead and cadmium can leach out of the cells and get into groundwater, as well as affect plants. These metals also have a record for detrimental effects on human health. Lead is commonly known to impair brain development in children, and cadmium is a carcinogen.
How Does A Pv Cell Work
Solar Photovoltaic cells generate electricity by absorbing sunlight and using that light energy to create an electrical current. The current created by all of the cells together adds up to enough electricity to power a typical home. Solar cells are made of silicon, which is a semiconductor material. Silicon is the most abundant element in the universe and is found in every cell of every living thing on the planet.
The silicon in a solar cell is made up of atoms that are arranged in an orderly pattern called a crystalline lattice. When sunlight hits a silicon cell, the electrons that make up the silicon atoms are attracted to each other, creating an electric current that can be used to charge a battery. This is how solar cells work, but they are not the only way to make electricity from sunlight.
Other methods of generating electricity, such as concentrating solar power, use mirrors to focus the suns rays into a concentrated beam that is then converted into electricity. Solar cells can also be made from other materials, including silicon carbide and carbon nanotubes , but these materials are more expensive and less efficient than silicon.
Recommended Reading: How A Solo Stove Works
What Are Solar Cells
Solar cells are also known as photovoltaic cells , which work to generate electricity directly from sunlight. This is different to photovoltaic thermal cells , which work to provide heat for water in the home. Photovoltaic cells are connected electrically, and neatly organised into a large frame that is known as a solar panel. The actual solar cells are made of silicon semiconductors that absorb sunlight and then convert it into electricity.
Currently, solar panels that are used for domestic purposes are only able to take around 20% of the sunlight that they receive and turn it into electricity. This is what is known as solar efficiency. There are several other forms of solar cell available that are used for commercial and industrial purposes. These are able to have an efficiency rating of up to 40%, but they do tend to be more expensive than domestic models.
One of the great things about solar technology is the fact that advances in the field are constantly being made, raising the overall quality and efficiency. It is expected that this will only increase with further research and development. Similarly, as these aspects increase, the price of solar panels is expected to keep falling making them available to a much wider number of people.
