How Far Does The Solar Wind Blow
The solar wind sweeps through the solar system far beyond the orbit of Pluto, forming a large “bubble” called the heliosphere. According to NASA, the heliosphere is shaped like a long wind sock as it moves with the sun.
The closest boundary of the heliosphere is about 100 AU out from the sun, according to an ESA statement . .
The heliosphere acts as a protective shield, defending us against cosmic rays consisting of energetic particles that can damage living cells. Comic rays are generated outside our solar system and blaze along at almost the speed of light. Without our protective bubble, these high-energy atom fragments would constantly bombard Earth. “Without the heliosphere, life would certainly have evolved differently – and maybe not at all,” says heliophysicst Richard Marsden in the ESA statement.
Architecture And Urban Planning
Sunlight has influenced building design since the beginning of architectural history. Advanced solar architecture and urban planning methods were first employed by the Greeks and Chinese, who oriented their buildings toward the south to provide light and warmth.
The common features of passive solar architecture are orientation relative to the Sun, compact proportion , selective shading and thermal mass. When these features are tailored to the local climate and environment, they can produce well-lit spaces that stay in a comfortable temperature range. Socrates‘ Megaron House is a classic example of passive solar design. The most recent approaches to solar design use computer modeling tying together solar lighting, heating and ventilation systems in an integrated solar design package.Active solar equipment such as pumps, fans, and switchable windows can complement passive design and improve system performance.
Rough Estimates Of The Solar Energy Available At The Earths Surface
The solar constant is the average extraterrestrial insolation at the edge of the atmosphere:
The Earth presents a disc of area nR2 to the Sun, therefore the total amount of extraterrestrial insolation incident on the Earth is ISC × nR2. This value is then divided by half the surface areas of the Earth, 4nR2/2, which gives 684 W/m2, the average insolation incident on unit area of the Earth facing the Sun . Note that solar panels are calibrated assuming that there is 1000 W/m2 available.
Figure 2.9: Radiation estimation.
A rough estimate of the irradiation incident per unit area of the Earths surface can be made if we assume that 30% of the Suns energy is lost in the atmosphere and that the a day is an average of 12 hours long at any location.
Or if we assume that the Sun is only at an appreciable strength for an average 6 hours in the day :
Figure 2.10 shows the yearly profile of mean solar radiation for different locations around the world. The solid grey line show the value of 5.75 kWh/day and the dashed grey line shows 2.88 kWh/day.
Figure 2.10: The yearly profile of mean solar radiation for different locations around the world.
Don’t Miss: Can I Add More Batteries To My Solar System
Solar Power Generation Technologies
As already outlined, there are two ways of turning the energy contained in sunlight into electricity. The first, called solar thermal power generation, involves using the sun simply as a source of heat. This heat is captured, concentrated, and used to drive a heat engine. The heat engine may be a conventional steam turbine, in which case the heat will be used to generate steam, but it could also be a closed-cycle turbine system using an organic thermodynamic fluid, a gas turbine, or a Sterling engine.
The second way of capturing solar energy and converting it into electricity involves use of the photovoltaic or solar cell. The solar cell is a solid-state device like a transistor or microchip. It uses the physical characteristics of a semiconductor such as silicon to turn the sunlight directly into electricity. The simplicity and durability of the solar cell makes it an extremely attractive method of generating electrical power.
Balasubramanian Viswanathan, in, 2017
| Solar electricity |
How Does The Suns Energy Reach The Earth
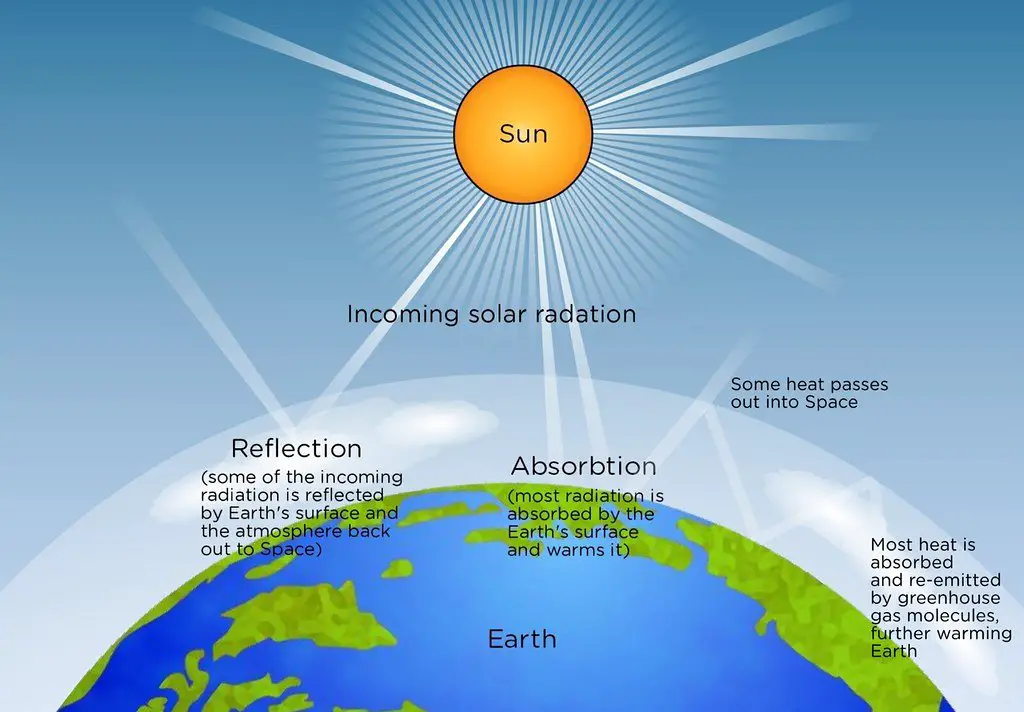
The Suns energy gets to the Earth through radiation which you can prove just by standing outside and letting the suns rays warm your face on a sunny day. The energy lost is emitted as light or electromagnetic radiation. Energy that is absorbed by an atom causes its electrons to jump up to higher energy levels.
Recommended Reading: How To Make Money Selling Solar Panels
We Are Currently Reliant On Materials From Earth But Scientists Are Also Considering Using Resources From Space For Manufacturing Such As Materials Found On The Moon
One proposed solution is to develop a swarm of thousands of smaller satellites that will come together and configure to form a single, large solar generator. In 2017, researchers at the California Institute of Technology outlined designs for a modular power station, consisting of thousands of ultralight solar cell tiles. They also demonstrated a prototype tile weighing just 280g per square metre, similar to the weight of card.
Recently, developments in manufacturing, such as 3D printing, are also being investigated for their potential in space power. At the University of Liverpool, we are exploring new manufacturing techniques for . A solar sail is a foldable, lightweight and highly reflective membrane capable of harnessing the effect of the Suns radiation pressure to propel a spacecraft forward without fuel. We are exploring how to embed solar cells on sail structures to create large, fuel-free power stations.
You might also like:
How Do Solar Flares Affect Earth
Different types of flares, particularly X-class flares, affect Earth, satellites and even astronauts.
Luckily for us, A and B-class solar flares are the most common and are also the weakest of the solar flare classes, too feeble to affect Earth in any significant way. C-flares are also fairly weak, exhibiting little or no effect on Earth according to SpaceWeatherLive.com.
With the two largest classes of flares, things start to get a little more interesting.
Strong M-class and X-class flares and can trigger coronal mass ejections a large release of plasma and magnetic field from the sun. This behavior can disrupt Earth’s magnetosphere and result in geomagnetic storms. Such geomagnetic storms can lead to auroras closer to the equator than is possible during calm conditions.
In 1989, a large solar flare accompanied a coronal mass ejection and hit Earth, plunging the entire province of Quebec, Canada, into an electrical blackout that lasted 12-hours, according to a NASA statement . The solar eruption triggered a geomagnetic storm on Earth, resulting in aurora borealis, or northern lights, that could be seen as far south as Florida and Cuba.
During an eruption, M-class and X-class flares can also cause minor to extensive radio blackouts on the side of Earth facing the sun. Radio blackouts mostly affect High Frequency radio communications though sometimes Very High Frequency and higher frequencies can be affected, according to SpaceWeatherLive.
Recommended Reading: Does Solar Really Pay For Itself
Climate And Earths Energy Budget
The Earths climate is a solar powered system. Globally, over the course of the year, the Earth systemland surfaces, oceans, and atmosphereabsorbs an average of about 240 watts of solar power per square meter . The absorbed sunlight drives photosynthesis, fuels evaporation, melts snow and ice, and warms the Earth system.
Solar power drives Earths climate. Energy from the Sun heats the surface, warms the atmosphere, and powers the ocean currents.
The Sun doesnt heat the Earth evenly. Because the Earth is a sphere, the Sun heats equatorial regions more than polar regions. The atmosphere and ocean work non-stop to even out solar heating imbalances through evaporation of surface water, convection, rainfall, winds, and ocean circulation. This coupled atmosphere and ocean circulation is known as Earths heat engine.
The climates heat engine must not only redistribute solar heat from the equator toward the poles, but also from the Earths surface and lower atmosphere back to space. Otherwise, Earth would endlessly heat up. Earths temperature doesnt infinitely rise because the surface and the atmosphere are simultaneously radiating heat to space. This net flow of energy into and out of the Earth system is Earths energy budget.
Earth System Models About The Absorption And Reflection Of Sunlight
This Earth system model is one way to represent the essential processes and interactions related to the absorption and reflection of sunlight. Hover over the icons for brief explanations click on the icons to learn more about each topic. the Earth system models on this page.
This model shows some of the changes to Earths surface and atmosphere that can affect the amount of sunlight that is absorbed or reflected. These changes influence the amount of heat that is re-radiated, and can also greatly influence the biosphere by altering the amount of sunlight available for photosynthesis.
Recommended Reading: How Much Does A Solar System Cost
Why Cant Photosynthesis Use Uv Or Infrared Light
Visible light is the only band of light on the spectrum to be considered photosynthetically active. It has the perfect amount of energy to excite the electrons needed to start photosynthesis and not damage DNA or break bonds.
Ultraviolet can not be used for photosynthesis because it has too much energy. This energy breaks the bonds in molecules and can destroy DNA and other important structures in organisms 8. When plants and other photoautotrophs attempt to use UV-A for photosynthesis, electron transport efficiency is decreased, which in turn decreases the rate of photosynthesis 6. On the other side of the spectrum, infrared light does not contain much energy. The insufficient energy does not excite electrons in molecules enough to be used for photosynthesis. Infrared light is converted to thermal energy instead 8.
How Deep Does Sunlight Reach In The Ocean
The ocean is split into three zones based on light. The first zone, the euphotic or sunlight zone, is where sunlight penetrates. Phytoplankton live in the euphotic zone because there is enough light for photosynthesis. This zone extends to about 660 ft below the ocean surface. 2
The next zone is called the dysphotic zone. Some light is able to reach this depth, but it is not enough for photosynthesis to occur 29.
The last zone starts about 3,300 ft below the oceans surface and is called the aphotic zone. Sunlight cannot reach this zone, and its only light comes from bioluminescent organisms 2.
You May Like: Does Having Solar Panels Save Money
How Deep Does Sunlight Reach In Freshwater
The depth that light penetrates in freshwater is dependent on water clarity. In waters with a high level of turbidity, or suspended solids, light will not reach as far as clear bodies of water. These suspended particles can both absorb and scatter light 1. In most rivers and streams, light will reach the riverbed, and photosynthesis can occur throughout the water column. However, in particularly deep, algae-covered or turbid lakes, light may not be able to reach certain depths.
Like the ocean, deep lakes are split into three zones. The first zone is called the littoral zone. This zone is close to the shore and sunlight reaches all the way to the bottom. Aquatic plants in the littoral zone can grow on the lake bed and still receive enough light for photosynthesis 19. The next zone is known as the limnetic zone and is the surface layer of open water. Photosynthesis can occur in this zone as it is penetrated by light. The depth of the limnetic zone depends on the turbidity of the water. In more turbid water, the limnetic zone will be shallower 19. Below the limnetic zone is the profundal zone. This is the benthic layer of a deep lake. Sunlight cannot reach this zone, so photosynthesis will not occur. Instead, organisms that permanently reside in the profundal zone rely on falling organic matter from higher zones 19.
How To Harness Solar Power

In one technique, long troughs of U-shaped mirrors focus sunlight on a pipe of oil that runs through the middle. The hot oil then boils water for electricity generation. Another technique uses moveable mirrors to focus the sun’s rays on a collector tower, where a receiver sits. Molten salt flowing through the receiver is heated to run a generator.
Other solar technologies are passive. For example, big windows placed on the sunny side of a building allow sunlight to heat-absorbent materials on the floor and walls. These surfaces then release the heat at night to keep the building warm. Similarly, absorbent plates on a roof can heat liquid in tubes that supply a house with hot water.
Solar energy is lauded as an inexhaustible fuel source that is pollution- and often noise-free. The technology is also versatile. For example, solar cells generate energy for far-out places like satellites in Earth orbit and cabins deep in the Rocky Mountains as easily as they can power downtown buildings and futuristic cars.
Don’t Miss: What Does Pv Mean In Solar Panels
Explore The Earth System
Click the icons and bolded terms on this page to learn more about these process and phenomena. Alternatively, explore the Understanding Global Change Infographic and find new topics that are of interest and/or locally relevant to you.
To learn more about teaching the absorption and reflection of sunlight, visit the Teaching Resources page.
Ice Climate Change And The Earths Energy Budget
Ice affects the entire earth system in a variety of ways. In the ocean and at the land-sea boundary, ice prevents relatively warm ocean water from evaporating, transferring heat to the colder atmosphere and thereby increasing global air temperature.
Image courtesy of Hugo Ahlenius, UNEP/GRID-Arendal Maps and Graphics Library.
Ice also reflects sunlight, thus preventing additional heat from being absorbed by water or land. The ice-covered polar regions are colder than other places on earth, due in part to the high albedo of the snow and ice cover.
As earths climate warms, ice in the form of glaciers and sea ice has decreased dramatically. Data generated from satellites that monitor the formation of polar sea ice indicate that both coverage and thickness have decreased over the past three decades. Recent studies show that the worlds highest glaciers are receding at an average rate of 10 to 15 meters per year. A study released in June 2008 indicates that Arctic sea ice extent shrank to a record low in the summer of 2007.
The decreasing extent of ice in the polar regions is part of a positive feedback loop that can accelerate climate change. Warmer temperatures melt snow and ice, which decreases earths albedo, causing further warming and more melting.
Recommended Reading: How Was The Solar System Formed
The Solar Energy Resource
Solar energy is generated by nuclear reactions within the body of the sun. This energy reaches the surface of the earth in the form of electromagnetic radiation. The composition of this radiation as it travels through space towards the earth is around 56% infrared, 36% visible radiation and 7% ultraviolet with the remainder belonging to regions of the electromagnetic spectrum outside the energy ranges covered by these three.
Not all this radiation reaches the surface of the earth. Some is scattered by dust and molecules in the atmosphere. This scattering is a random process, sending the radiation in all directions so that much goes directly back into space. The remainder reaches the surface, but as diffuse, indirect radiation. Clouds act to reflect more sunlight back into space and they play an important role in regulating the temperature on the surface of the earth.
Another part of the radiation is absorbed by molecules such as water, carbon dioxide, ozone and oxygen within the atmosphere. Water and carbon dioxide absorb energy from the infrared region, while oxygen and ozone absorb from the ultraviolet. All these interactions reduce the solar energy flux by around 40% while at the same time changing its composition so that the sunlight which reaches the earths surface comprises 50% visible radiation and 47% infrared.
Table 13.2. Solar Energy and the Earth
: World Energy Council.
Paul Denholm, … Mark Mehos, in, 2010
The Hole In The Ozone Layer
Ozone is a molecular gas composed of three oxygen atoms . This gas helps protect Earth because it absorbs most of the suns ultraviolet radiation. The majority of UV-C, most of UV-B and about half of UV-A are absorbed by oxygen and ozone in the ozone layer. This layer is primarily found in the stratosphere, between 10 and 50 km above Earths surface.
The hole in the ozone layer is found in the atmosphere over the Antarctic. This area is not completely void of ozone, but is instead a patch of atmosphere that possesses a significantly lower level of ozone than normal 27. While the cause of gap is sometimes a subject of debate, studies have shown that ozone is destroyed when it reacts with chlorine, nitrogen, hydrogen, or bromine 27. When these chemicals enter the atmosphere, they can remove the ozone present. Regardless of its cause, the hole in the ozone layer allows more UV radiation to reach Earth. If the increase in UV radiation becomes excessive, it can be harmful to both terrestrial and aqueous habitats 27.
Recommended Reading: Do Solar Panels Give Off Heat
Its Reliable Free And Clean But
Solar energy is likely to continue to exist so far into the future that we can think of it as being unending. Essentially, its renewable, unlike fossil fuels which are running out as we use them.
In addition, using solar energy doesnt cause air pollution or involve damaging the Earths surface. It requires no difficult and expensive extraction procedures. Creating the solar cells themselves does require resourcesconverting sand into silicon still requires considerable energybut this is paid back within three or four years of a solar cells operation.
But the main problem is what to do when the Sun doesnt shine. Although we consume a considerable amount of electricity during the day when the Sun is readily available, we also need storage to tide us over on cloudy days and at night-time. On a domestic scale, the frontrunner in batteries to complement a rooftop solar panel set-up is currently the Tesla Powerwall. There are some other strong contenders in the products being rolled out by Panasonic and LG Chem.
