Other Incentives For Going Solar
The federal credit is the easiest solar tax incentive to qualify for but you might qualify for state and local solar tax incentives as well.
Most state and local credits and rebates wont reduce your federal credit but may increase your federal taxable income since youll have less state and local income tax to deduct. These homeowner tax benefits make it easier to recoup the upfront costs of installing solar panels.
Summary Data For Ontario
| Average retail electricity price | 16.32 cents / kWh |
| Average annual consumption per household | 8,580 kWh |
| Yes |
Ontario is the leader for grid-connected PV systems in Canada. Thanks to generous feed-in tariff programs, solar energy really took off in the province. While those feed-in tariff programs are now closed, homeowners and businesses in Ontario will soon benefit from the new GreenON Solar Rebate program .
At 16.32 cents/ kWh, the electricity prices in the province are above the national average of 12.61 cents / kWh. When it comes to average electricity consumption per household, residents of this province consume 8,580 kWh per year, below the national average of 13,300 kWh.
Currently, Ontario has 3 financial incentive programs and 1 regulatory programs supporting the adoption of solar energy.
Ontario is a grid parity province, making solar power cheaper than the residential utility rates. The incentives listed below can significantly reduce the cost of installation of solar panels for your home or business.
Form 5695 Instructions: The 3 Steps To Claim The Solar Tax Credit
There are three broad steps youll need to take in order to benefit from the federal solar tax credit:
Make sure you have enough tax appetite to use the federal ITC against your total taxes.
This form validates your qualification for renewable energy credits, and can be obtained online.
Loop your renewable energy credit information into your regular tax form.
Also Check: How Do Solar Panel Kits Work
History Of The Solar Investment Tax Credit
In the early days of solar energy, residential systems were far more expensive than they are now. By many homeowner standards, however, theyre still expensive today. For example, in 2009, it cost $8.50 per watt to install solar panels the current cost per watt, as of publishing, is about $2.40 to $3.22.
This point-of-entry cost into the world of renewable residential solar power dramatically limited the number of homeowners who could take advantage of solar for their home.
The solar investment tax credit was established by the Energy Policy Act of 2005, which established standards for renewable fuels, mandated an increase in the use of biofuels and established renewable energy-related tax incentives.
Under this law, the original policy was set to expire at the end of 2007. However, the solar ITC has been so popular that its expiration date has been extended multiple times.
Solar panel costs have decreased dramatically in the last 20 years, but the ITC can still save individuals and businesses a great deal on their federal taxes.
Today, solar systems are far less expensive due to changes in the industry and the manufacturing of certain parts that make up the solar system. Solar panels, lithium batteries and inverters are all far less expensive to make and buy now than they were in those early days.
What Are Tax Exemptions For Solar
Solar tax exemptions include both property and sales tax exemptions provided by state and local governments to individuals and companies that install solar energy property. Property tax exemptions allow businesses and homeowners to exclude the added value of a solar system from the valuation of their property for taxation purposes.
You May Like: Do I Need A Tax Id Number For Sole Proprietorship
How Do I Claim The Solar Panel Tax Credit To Claim My Rebate
So lets get to the good stuff. What do you need to do to actually get your hands on this money and reduce the total cost?
Our first bit of advice is to keep all your receipts from the start of your solar installation project. Like any tax incentive, the Federal Solar Tax Credit requires a paper trail. The more you spend on your project, the larger your credit so make sure to keep track of everything!
Here are some of the expenses that you are allowed to claim:
- Solar equipment
Compare Solar Options On Energysage
Interested in seeing how much you can save with solar rebates? Sign up on the EnergySage Marketplace to receive up to seven quotes from local, pre-screened installers. These quotes will include incentives you may be eligible for, including the federal tax credit and applicable local incentives. If youd prefer to start with an estimate of solar costs and savings, try our Solar Calculator.
Recommended Reading: Do Solar Panels Have To Go On The Roof
An Overview Of Solar Rebates
Like other types of rebates, solar rebates are incentives paid upfront for installing solar. Solar rebate incentive values can range anywhere from hundreds to thousands of dollars, helping property owners achieve an even quicker payback on their solar investment.
Rebates not only vary in value, but in how the value is determined: sometimes, governments or utilities offer rebates in fixed amounts, but more often than not, the rebate you receive depends on the size of your solar panel system. States, municipalities, or utility companies offering solar rebates often structure the incentive as a set dollar amount per kilowatt of solar installed, offering different values for residential versus commercial solar panel systems.
Importantly, not everyone who installs a solar panel system will receive a rebate: these incentives tend to be locally-based, so your eligibility is dependent upon where you live.
Here’s How To Take Advantage Of The Solar Tax Credit Extension In 2021
Get all the details on the US government’s tax credit for residential solar panels.
If you’re thinking about installing solar panels, you may have heard of the solar Investment Tax Credit, also called the federal solar tax credit. The current federal solar tax credit guidelines were extended through 2022 when former President Donald Trump signed the Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2021 this past December. That’s good news for anyone interested in getting a residential solar panel set up in the next couple years at the same 26% tax credit as 2020.
Burning coal, oil and natural gas for heat and electricity accounts for roughly 75% of US greenhouse gas emissions. These pollutants contribute to rising global temperatures and sea levels, changes in weather patterns and other factors associated with climate change.
Renewable alternatives, such as geothermal energy, wind power and solar power, reduce the footprint caused by these fossil fuels. Various incentives exist in the US for commercial and residential use of renewable energy, including the federal solar tax credit. President Joe Biden has already signaled strong interest in environmental issues by rejoining the Paris Climate Agreement on his first day in office. That suggests the 26% federal solar tax credit might be extended beyond its current deadline at the end of 2022, but the Biden administration hasn’t made any changes to the federal solar tax credit .
Read on to learn how to take advantage of this tax credit.
You May Like: How Much Do Commercial Solar Panels Cost
The Framework If Approved Would Represent The Largest Single Investment In The Clean Energy Economy In The Us President Biden Has Said
Build Back Better, if passed in its current form, will include rebates for homeowners who embrace electric heat pumps and other forms of cleaner energy.
A handful of programs in the recently-passed infrastructure bill aim to help U.S. homeowners and renters heat and cool their homes, cook meals, and even shower all while using less energy.
But its the $2 trillion budget reconciliation bill, which Democrats have called Build Back Better, that packs the most energy-saving carrots for individuals and families, and which are meant to push the nation toward net-zero emissions by 2050.
The House passed its version of Build Back Better Friday the bill now goes to the Senate, where it faces opposition from Republicans and an uphill battle against some middle-of-the-road Democrats in a closely divided chamber.
The administrations Build Back Better bill includes $555 billion in tax credits, spending and other incentives to promote wind and solar powerICLN, +0.41% , electric vehicles, climate-minded agriculture and forestry programs and other clean energy ideas, some at the federal and community level and some earmarked for American homes.
And:5 takeaways from the COP26 climate summit investors need to know
All of this is a gradual process.
Steven Nadel, executive director at the American Council for an Energy Efficient Economy
Rebates for clean-energy upgrades at home
All of this is a gradual process, he added.
Other features in Build Back Better
Direct Economic Benefits Are Less Widely Shared
While Biden’s proposed solar policies spread costs broadly across US taxpayers, they allocate direct economic benefits more narrowly. The Clean Electricity Performance Program specifically targets electric utilities that sell power to homes, businesses, and other end users.
Under the economic plan that Congress is now considering, utilities that grow the share of clean energy in their retail sales compared to the previous year would receive payments based on the amount of clean electricity they add. Utilities that fail to meet the growth target would pay penalties based on how far they fall short.
Electric utilities own many of the country’s existing, mostly fossil-fueled power plants. Most have been reluctant to promote solar, which would reduce demand for electricity from their own power plants.
But the Clean Electricity Performance Program does not cover another category of power company, called non-utility generators. Instead of selling power to end-use customers, these companies sell electricity to utilities, marketers, or brokers. Non-utility generators provide over 40% of US power and have driven much of the recent deployment in solar and other renewables.
Non-utility generators may benefit indirectly if utilities buy solar power from them to comply with the Clean Electricity Performance Program. But by focusing on utilities, the program threatens to alienate non-utility generators and stifle competition.
Don’t Miss: When Is The Best Time To Install Solar Panels
The History Of The Federal Solar Investment Tax Credit
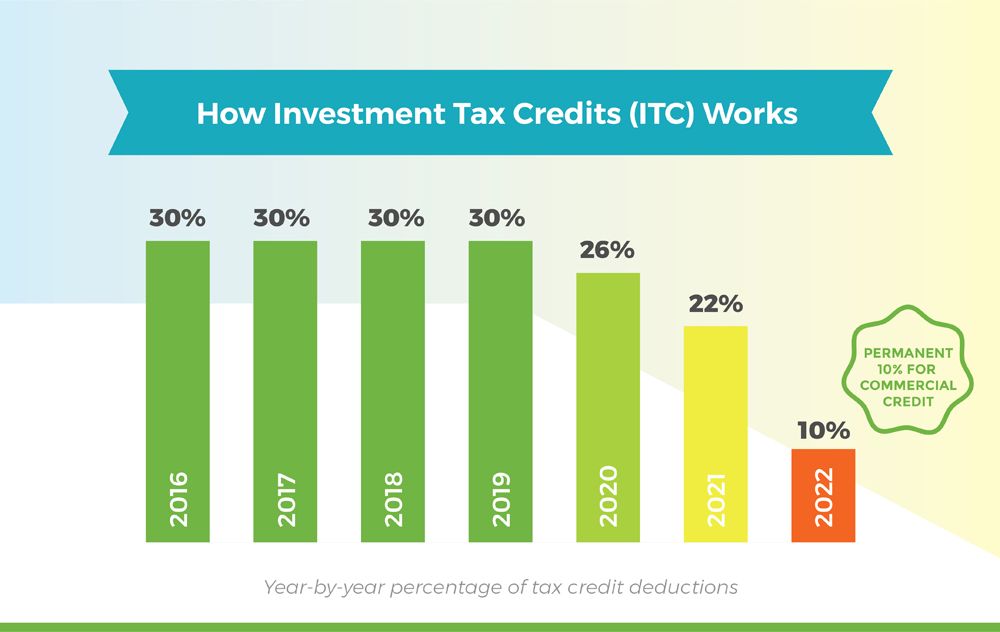
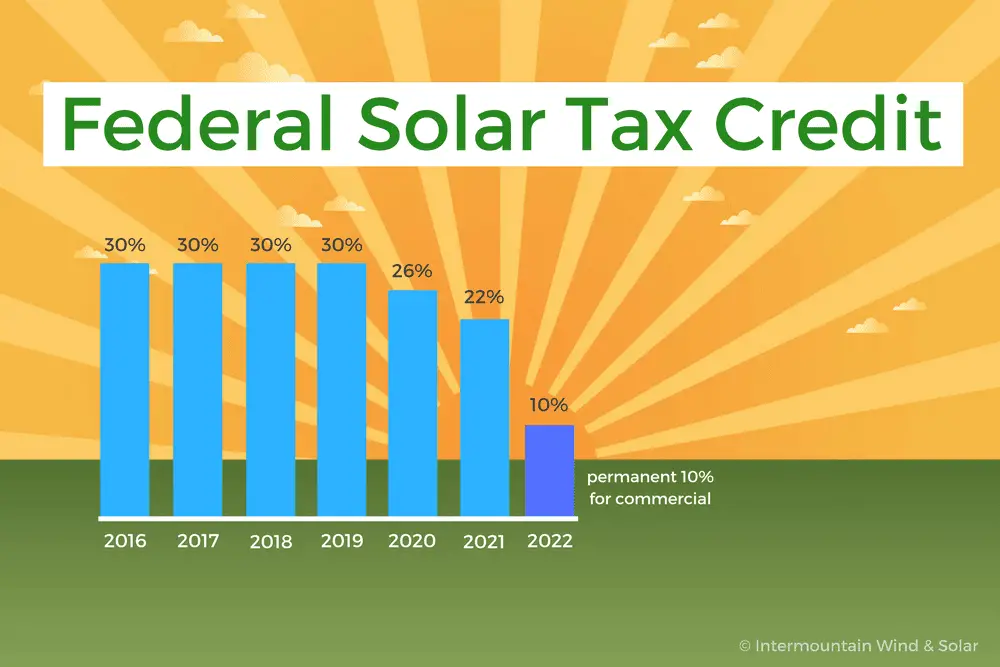
The ITC was originally established by the Energy Policy Act of 2005 and was set to expire at the end of 2007. Thanks to the popularity of the ITC, and its success in supporting the United States transition to a renewable energy economy, Congress has extended its expiration date multiple times, including most recently in December 2020 to extend the ITC at 26 percent for two additional years. Now, the solar investment tax credit is available to homeowners in some form through 2021. Here are the specifics:
- 2016 2019: The tax credit remains at 30 percent of the cost of the system.
- 2020-2022: Owners of new residential and commercial solar can deduct 26 percent of the cost of the system from their taxes.
- 2023: Owners of new residential and commercial solar can deduct 22 percent of the cost of the system from their taxes.
- 2024: Owners of new commercial solar energy systems can deduct 10 percent of the cost of the system from their taxes. There is no federal credit for residential solar energy systems.
What Is A Tax Credit
A tax credit is a dollar-for-dollar reduction in the amount of income tax you would otherwise owe. For example, claiming a $1,000 federal tax credit reduces your federal income taxes due by $1,000. The federal tax credit is sometimes referred to as an Investment Tax Credit, or ITC, though is different from the ITC offered to businesses that own solar systems.
Also Check: How Does Residential Solar Power Work
Are You Eligible To Claim The Federal Solar Tax Credit
In order to claim the federal solar tax credit and get money back on your solar investment, you have to meet the following criteria when filing your 2021 taxes:
- Your solar PV system must have been installed and began operating at some point between January 1, 2006, and December 31 of this year.
- Your system must be installed at either your primary or secondary residence.
- You must own the solar PV system, whether you paid upfront or are financing the cost.
- The solar system must either be brand new or have been used for the first time. You only get to claim this credit once, for the “original installation” of your solar PV equipment.
Things To Know About The Federal Solar Power Tax Credit
More and more accountants are recommending their homeowner clients consider solar panels. Heres why.
When solar panels are installed on rooftops, the sun beats down on them, producing electricity that can potentially help homeowners save money on monthly electric bills and reduce their carbon footprint. This solar-generated power is used in the home first, and any excess can be fed into a battery instead of back to the grid, which means homeowners will have access to this power during outages. The battery backup can be a potential significant cost savings when you consider monetary losses that could result from spoiled food, medication or the inability to work from home.
In 2005, the federal solar investment tax credit was established, and it has been extended multiple times since. When it first passed, the value of the credit was at 30 percent, but it fell to 26 percent in 2020. The latest extension of the solar tax credit came last December, and it gives homeowners and businesses up to a 26 percent credit on the net cost of a solar system. The 26 percent credit is in effect for two more years before it drops to 22 percent in 2023 and sunsets altogether for homeowners in 2024. The credit for businesses follows a similar path, with the exception being that its credit falls to 10 percent in 2024 and will stay at that number in future years.
Below are four things you need to know when advising your clients:
Read Also: How Many Solar Panels For 800 Sq Ft Home
What Qualifies For The Solar Tax Credit
- The entire bill for a qualified system, minus the sales tax. That includes solar panels labor costs for on-site preparation, assembly, and installation of the system and piping or wiring to connect the system to your house.
- Installation of a solar system in a primary or second house.
- Systems purchased outright or with a loan.
- Solar roofing tiles, like those being sold by Tesla.
- Solar installed in a property that you live in for at least part of the year. That could cover, for instance, a second home that you rent out when youre not there. The credit is prorated based on how much time you spend in the residence. For a multifamily home in which you live but also collect rent, you may be eligible for either the residential or business tax credit, depending on how much of the property is used for business. Check with a tax expert for details.
Getting Your States Tax Credit
Many states also offer tax credits for solar some will continue even after the federal credit expires. Arizona and Massachusetts, for instance, currently give state income tax credits worth up to $1,000 toward solar installations. New York offers a state tax credit of up to $5,000. Marylands is $1,000 per system, plus 30 percent of the cost to install a giant battery to store the energy thats produced.
For details on your states programs, go to your states tax authority website, or to dsireusa.org, a catalog of all state energy incentives run by the North Carolina Clean Energy Technology Center.
Read Also: How Much Power Does A 300 Watt Solar Panel Produce
Getting The Federal Tax Credit
With the Renewable Energy credit, you simply subtract your credit amount from the total tax the IRS says you must pay.
Its different from a tax deduction, which reduces the amount of income you pay taxes on. A $100 credit is worth $100 regardless of your tax rate, says Kevin Martin, principal tax research analyst at H& R Block in Kansas City, Mo.
If you cant use all of the credit in one year, you can carry it over into later years, Martin says. If, say, your federal taxes are $6,000 for 2020 and youre eligible for a $7,000 tax credit for installing a solar system at your house, you can claim the leftover $1,000 as a credit toward your 2021 taxes.
But not every type of solar installation or expense is eligible for the tax credit. Qualified solar systems that meet IRS guidelines and produce electricity and heat water are covered.
Start Your Solar Journey Today With Energysage
EnergySage is the nations online solar marketplace: when you sign up for a free account, we connect you with solar companies in your area, who compete for your business with custom solar quotes tailored to fit your needs. Over 10 million people come to EnergySage each year to learn about, shop for, and invest in solar. .
Read Also: How Solar Energy Works Step By Step
Is The Solar Itc Refundable
The solar ITC is not a refundable credit it can only be used against your organizations U.S. federal income tax liability.
However, the solar ITC may be carried back one year and forward up to 20 years for companies that dont have sufficient tax liability to offset for the tax year their solar energy system was placed in service.
A deduction is allowed for 50% of any portion of the solar ITC that remains unused after the 20-year carry forward period.
