In An Ac Sine Wave Whenever The Wave Crosses The Horizontal Axis Well Have A Zero
So, in this type, as opposed to a Random Turn-On type relay, when the input is active, it does not conduct the load current immediately
but the output will wait for the first zero-crossing point of the AC load voltage, to pass the whole electrical current toward the load.
In both Random Turn-On and Zero-crossing types of SSRs, when the control voltage is removed from the input terminals, the output will not stop passing the load current until the next zero-crossing point of the wave reaches.
Solid State Relays 9 Answers For Beginners
I cant forget the factory I worked at in my after graduation period. It was a plastic pipes factory. It depends on solid state relays to control production lines heaters. Many of solid state relays in the control panels switching on and off very fast.
The most important task in the factory was to check theses relays hourly. We used current clamp meter to check if the SSR is working or not. It has been more than 10 years ago when I left this factory to a better working chance. I decided to make some searching analysis about SSR, and I found some basic, but important, questions you should know.
In this article I will answer these important questions. Lets get started.
How To Use A Solid State Relay
Here’s how to use an SSR or Solid State Relay to control loads like vacuum tables, coolant pumps, heated 3D printing beds, dust collection systems and much more.
Note, an SSR only works with single-phase AC loads and will not switch DC loads. DC loads can be switched directly with the Buildbotics controller’s built-in DC load switches.
A small low current DC voltage control signal from a microcontroller or CNC controller can be use to control a much larger high current high voltage AC load using an SSR or Solid State Relay. This is handy for controlling vacuum tables, coolant pumps, heated 3D printing beds, dust collection and much more with GCode commands.
Inexpensive SSR devices with input voltages in the 3-32VDC range can be found on or at Sparkfun.
Don’t Miss: Is Free Solar A Scam
Advantages & Disadvantages Of Solid State Relays
As with any technology, there are advantages and disadvantages to their use. This is true for solid state relays – whilst they offer many advantages over other alternatives like electromechanical relays, they do have some drawbacks. The actual choice of technology must be considered looking at all the options so that the right choice is made.
Advantages of solid state relays
- Provides physical isolation between circuits.
- Faster switching than electromechanical relays. Switching time is typically around 1 ms
- Higher life expectancy than for electromechanical relays
- They do not suffer from the contact bounce experienced when using electromechanical relays.
Disadvantages of solid state relays
- Resistance in the output circuit is normally higher than that of an electromechanical relay
- Not as resilient to transient spikes and other overload conditions as a mechanical relay – unless protected, a transient above the limits of the output device could destroy the solid state relay.
Solid State Relay Basics
Solid state relays can have a variety of different devices at the core of their electronic circuits: thyristors of SCRs, triacs, bipolar junction transistors, BJTs, and MOSFETs provide ideal electronic switches within the solid state relay.
To provide the switching signal between the input and the switching element, an optical link is normally used. This gives virtually complete electrical isolation between the input and output circuits.
Often the switching device thryristor, triac, bipolar junction transistor or MOSFET is an optical version of the device that turns on in the presence of light.
Essentially the solid state relay is a switch where the input or control voltage lights up a light emitting diode. This acts as the transmitter of an optocoupler which then controls a switching device: thyristor, triac, bipolar transistor of MOSFET.
The solid state relay comprises a transmitter, Tx, and receiver, Rx. These are physically positioned within the solid state relay. The incoming control signal energises the LED within the optocoupler and this illuminates the output switching device which is photosensitive and this causes it be switch over from its normally non-energise state. Typically it switches the output device on, allowing current to pass through the SSR output.
The transmitter and receiver are typically located within the same electronic component, simplifying the construction of the solid state relays.
There are two main areas of the solid state relay:
Recommended Reading: Do Solar Panels Work With Snow On Them
Solid State Relay Working
The working of the solid-state relays can be understood by categorizing the solid-state relays into two categories. One is the AC solid state relay and the other is the DC solid state relay. It consists of one input and output terminals. The inputs and the output of the relay are attached to the specified terminals. When a specific control signal is provided to the input terminals of the solid-state relay, the ON and OFF function on the output terminal is performed accordingly and after attaining that function the switching function of the relay is turned ON. With the help of the coupling circuit in the solid-state relay, a channel is formed between the input and output of the relay.
The cutoff function is also performed by this coupling circuit in case of the unwanted or uncertain situations which are set initially before installing the relay. Optical couplers are used in the coupling circuit of the solid-state relay. The optical couplers have good sensitivity, higher response speed, higher input, and output insulation levels. The load used in the solid-state relay is a LED which is used to match the level of the input signal. The output is either 0 or 1 in the solid-state relay. The output of the solid-state relay is connected with a computer for interfacing.
Solid State Relay Working
Note: In A Future Article Youll Learn That Ssrs Are Usually Used With Another Type Of Controller Known As The Pid Controller
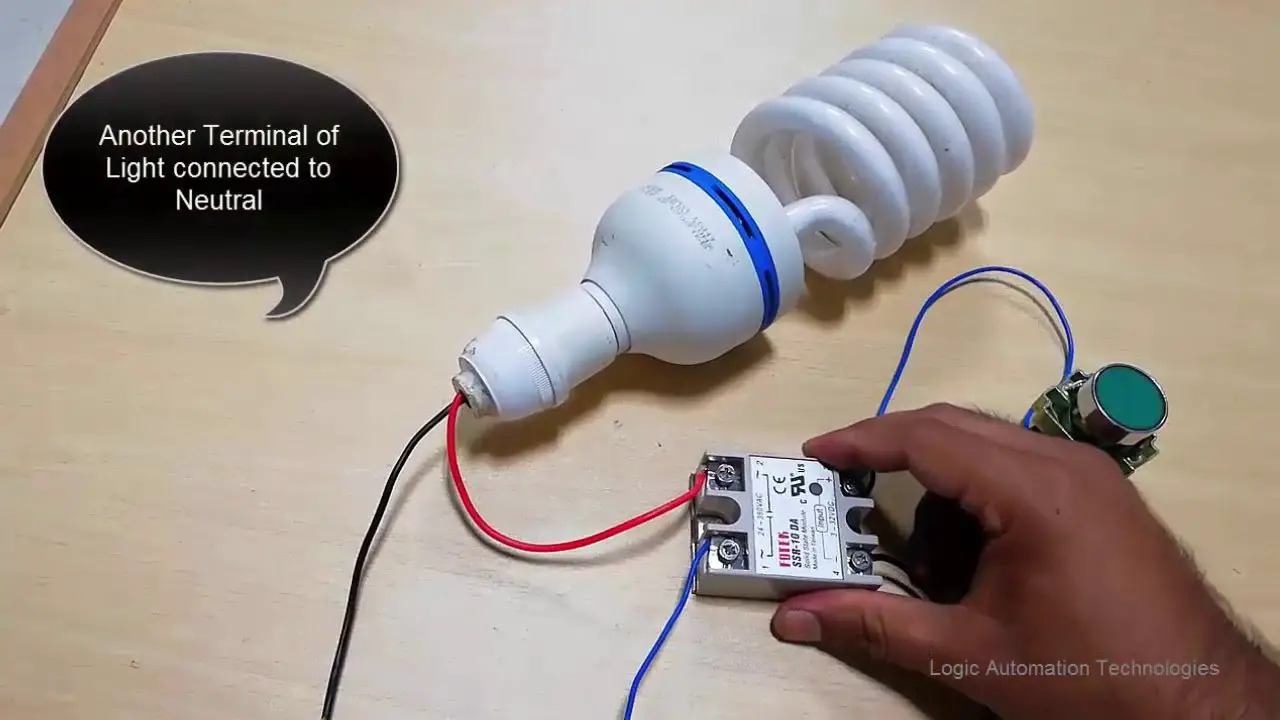
The heater will get its power from the AC power source but via the SSR. We transfer the live wire to the heater via the SSR.
So, we connect the Live wire from the power source to one of the output terminals of the SSR and will wire its other terminal to the heater.
The Neutral wire will be directly connected to the heater from the power source.
Here, you have to make sure to cover the terminals of the SSR as it has electrical power all the time even when the relay output is switched off.
As soon as the PLC sends the command, the SSR LED turns on, showing the output of the relay is closed.
So, the heater turns on and starts warming up to increase the temperature.
Of course, there is a sensor to feedback the temperature of the tank to the PLC.
Don’t Miss: Does Pine Sol Kill Lice
Synchronous & Random Switching Solid State Relays
When switching high currents and using semiconductor devices that can turn from off to on very quickly gives rise to sharp edges on waveforms. In turn this can lead to high levels of electromagnetic interference, EMI. As all devices these days must be designed to minimise this interference, it is necessary to utilise ways that minimise the generation of this EMI, so that the electromagnetic compatibility, EMC performance of the device falls within the required limits.
One method that can be used with AC and resistive loads, is known as synchronous or zero crossing switching. As the name indicates the solid state relay only turns on or off at the zero crossing point of the AC waveform irrespective of the input control signal timing.
Whilst zero crossing SSRs are ideal for resistive loads, they do not work properly with inductive loads because the current and voltage are out of phase. Often they do not turn off properly.
For inductive loads, like transformers and motors, it is normal to use random switching solid state relays. These devices turn on or off at the instant required by the input control signal and they do not take account of the position on the waveform.
What Are Dual Solid State Relays
Dual SSR by celduc allows to control two loads with a unique or separated input, in a single package. Many options are available: both vertical and horizontal connections, different input connectors & several output protections. Dual SSR can cover all the market needs!
A Dual SSR of the SOB series are two working single phase Solid State Relays into one standard 45mm package.
Also Check: How To Use Solar Energy At Home
What Is A Solid State Relay
Solid State Relay is an integrated contactless electronic switch device that is compactly assembled from an integrated circuit and discrete components. Depending on the switching characteristics of the electronic components , the SSRs are able to switch the “ON” and “OFF” state of the load very quickly through the electronic circuit, just like the function of traditional mechanical relays. Compared with the previous “coil-reed contact” relay, namely Electromechanical RelayEMR), there is no movable mechanical part inside the SSR, and there is also no mechanical action during the switching process of the SSR. Therefore, the Solid-State Relay is also called “non-contact switch“.
The structural characteristics of the SSR switch make it superior to the EMR. The main advantages of solid state relays are as follows:
The semiconductor component acts as a switch for the relay, which is small in size and long in life .
Of course, solid state relays also have some disadvantages, including: exist on-state voltage drop and output leakage current, need heat dissipation measures, higher purchase cost than EMR, DC relays and AC relays are not universal, single control state, small number of contact groups, and poor overload capability. While some special customized solid state relays can solve some of the above problems, these disadvantages need to be considered and optimized when designing circuits and applying SSRs to maximize thebenefits of solid state relays.
Benefits And Limitations Of Solid State Timers
One of the main advantages of solid state timers is the lack of mechanical or moving parts in the device. Since there is no opening or closing of contacts, solid state timers are not susceptible to mechanism wear such as arcing and pitting. As a result, solid state timer relays can operate for countless on/off cycles without deterioration in performance.
In addition, with no moving parts, noise is eliminated. The silent operation of solid state timers is especially beneficial in power cabinets that may contain dozens of timer relays. Additionally, the lack of mechanical components means that solid state timers offer significantly faster response times than their electromechanical counterparts. Instant-on solid state devices can typically communicate on/off signals from the control circuit to the load circuit in under 20 microseconds, making them ideal for fast-acting electronic devices.
Furthermore, most solid state timers require significantly less power than electromechanical switches to activate the control and load circuits. For instance, most solid state timers can actuate load circuits with as little as one milliamp in the control circuit with voltages as low as three volts DC.
The disadvantages of solid state timers can be considered to be minor, depending on the specific application. Some of these include:
If you would like to learn more about Amperites solid state timers and how they can be used in your electrical application, feel free to contact us.
Don’t Miss: When Can I Introduce Solid Food To My Baby
Insulation Resistance / Dielectric Strength:
1) Insulation resistance refers to the measured resistance value between the input terminal and the output terminal of the solid-state relay when a certain DC voltage is applied. It can alsoinclude the measured resistance value between the input terminal and the outer casing , and the measured resistance value between the output terminal and the housing.
2) Dielectric Strength, or dielectric withstand voltage, refers to the maximum voltage value that can be tolerated between the input terminal and the output terminal of the solid-state relay. It can also include the maximum voltagethat can be tolerated between the output terminal and the housing, and the maximum voltage that can be tolerated between the input terminal and the outer casing.
Attentions When Testing Solid State Relays

1) First the relationship between the output current and the shell temperature should be known before testing to avoid permanent damage to the SSR caused by overload, because the rated output current will drop when the casetemperature rises or with no radiator.
2) When testing the turn-on and turn-off voltage of DC-SSR, the input voltage cannot remain in the state between on and off for too long, otherwise the power consumption of the output terminal risessharply and burns out the output switching components.
3) Do not arbitrarily speed up the action rate during the test , otherwise the SSR relay will not work due to the large dynamic-switching-loss, or even the output switching components will be burnt out.
4) The solid state relays cannot achieve complete isolation between the output terminals in the off state, and therewill be a certain at the output terminal. When the dielectric withstand voltage and insulation resistance are tested at a higher voltage, it is prone to electric shock, so the insulation resistance or the withstand voltage must not be tested on the output terminals.
Read Also: How Much Does A Solar Panel Battery Cost
Output Voltage Drop / Output Leakage Current:
1) The output voltage drop is the measured output voltage at the rated operating current when the solid-state relay is in the on state.
2)The output leakage current refers to the measured current value that flowing through the load, under the condition that the solid-state relay is in theoff state and the rated output voltage is applied to the output terminal. This parameter is an indicator of the quality and performance of solid-state relays. The smaller the output voltage drop and the output leakage current, the better the solid-state relay.
Applications With An Ssr
Fig. 9-14 and 9-15 show typical contactor applications using an SSR.
Fig. 9-14. Start-stop contactor using an SSR.
Fig. 9-15. Starting an AC motor using an SSR.
In fig. 9-14 we see an SSR being used as with classic push button control. After pressing start the SSR output is closed. R1 is a limiting resistor for the input circuit. The voltage across Zb together with R2 and the stop push button function as a hold on until the stop button is pressed. Note that here an SCR with an AC input is needed.
For the three phase circuit shown in fig. 9-15 only two SCRs are used. If there was an SSR in each line it would be difficult to switch since the output thyristors of the SSR would only be fed from one side, in other words there would not be any voltage across the thyristor. In fig. 9-15 a mechanical three phase switch is needed to ensure the motor and relay are voltage free.
Charles J. Fraser, … , in, 1994
Recommended Reading: How To Calculate Batteries For Solar System
What Is A Solid State Relay And Why Do We Use Them
The look is quite a bit different from electromechanical relays the same as its manufacturing technology.
As its mentioned, there is no mechanical moving part used in Solid State relays manufacturing and all are made of semiconductors such as diodes, Transistors, Thyristors, Triacs, and so on.
There are different designs for different usages.
For example, when youre designing an electrical control panels internal layout, you always need more space.
And there is a slim design for Solid State Relays that would be an appropriate choice for you!
If you replace the EMRs with the slim design of the SSRs then youll have more spare space in your panel to add more hardware.
You can use Solid State Relays as an interface between your PLC output cards and the loads out there in the process.
However, as youll learn in the future articles, the Thyristors, and Triacs are more intended to drive the resistive heating elements and therefore the Solid-State Relays which use these electronic parts in their output circuits, are also more applicable for these purposes.
They also have different names depending on their manufacturer. For instance
Photo Relays,
and so on.
Emrs And Their Drawbacks
An electromechanical relay energizes a coil wound on an iron core to control the position of an armature. For a normally open output, the energized coil forces the armature to put the electrical contacts into the ON state. When the coil is de-energized, springs can move the contacts back to the OFF position.
Figure 1. In an EMR, the energized coil moves the armature to either connect or disconnect the output terminals.
An electromechanical relay is robust and versatile. However, it takes up more room and is slower than an SSR. Typically, an EMR needs 5 to 15 ms to switch and settlea delay which is not acceptable in some applications. Moreover, due to their moving parts, EMRs have a shorter operational lifetime.
An electromechanical relay uses magnetic fields to provide isolation an SSR, in contrast, achieves this goal generally through opto-coupling. As shown in Figure 2, in an SSR a small input voltage, typically 3 to 32 VDC, is used to illuminate an LED. When the LED is turned on, an output photo-sensitive device, such as a TRIAC, turns on and conducts current.
Figure 2. The basic structure of an SSR. Image adapted from pc-control.
An SSR can be designed to switch a DC or an AC load, and some types are capable of switching both AC and DC loads. An SSR’s output type is determined by the type of switching device: a transistor , an SCR, or a TRIAC.
Also Check: Where Do Solar Panels Come From
